Enterprise Resource Planning
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become indispensable tools for businesses aiming to streamline their operations and enhance their efficiency. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore ERP systems in detail—covering their definition, core features, benefits, implementation considerations and future trends. By the end of this blog, you will have a thorough understanding of how ERP systems can transform your business.
What is an ERP System?
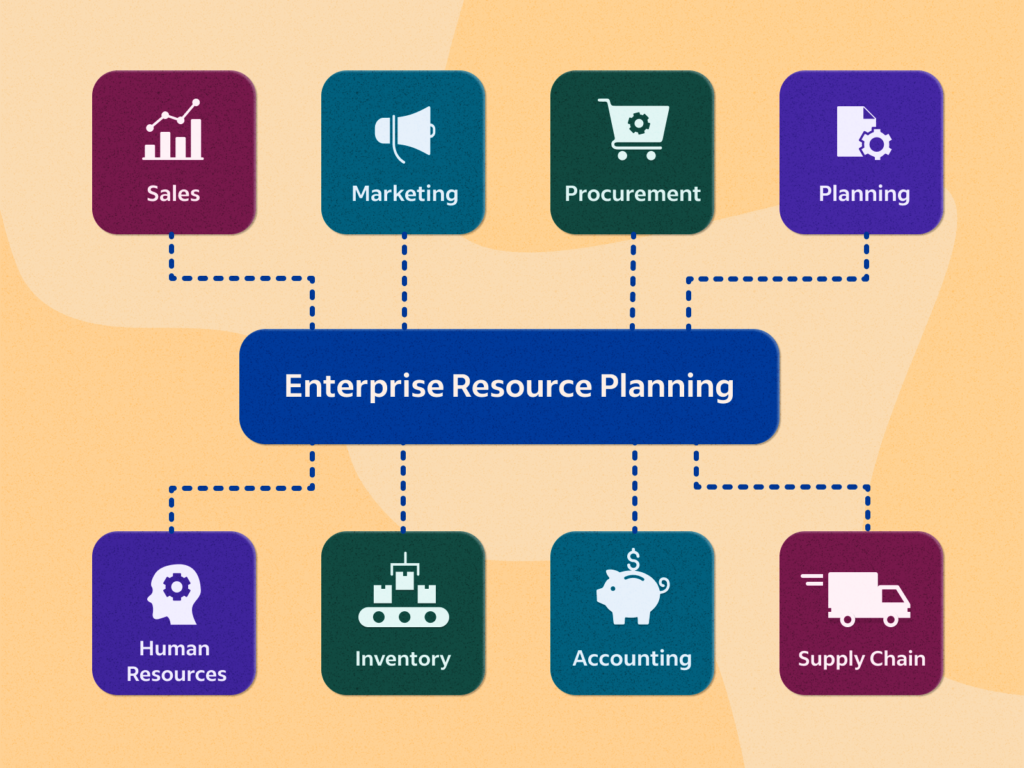
An ERP system is a suite of integrated software applications designed to manage and automate a company’s core business processes. These processes can include:
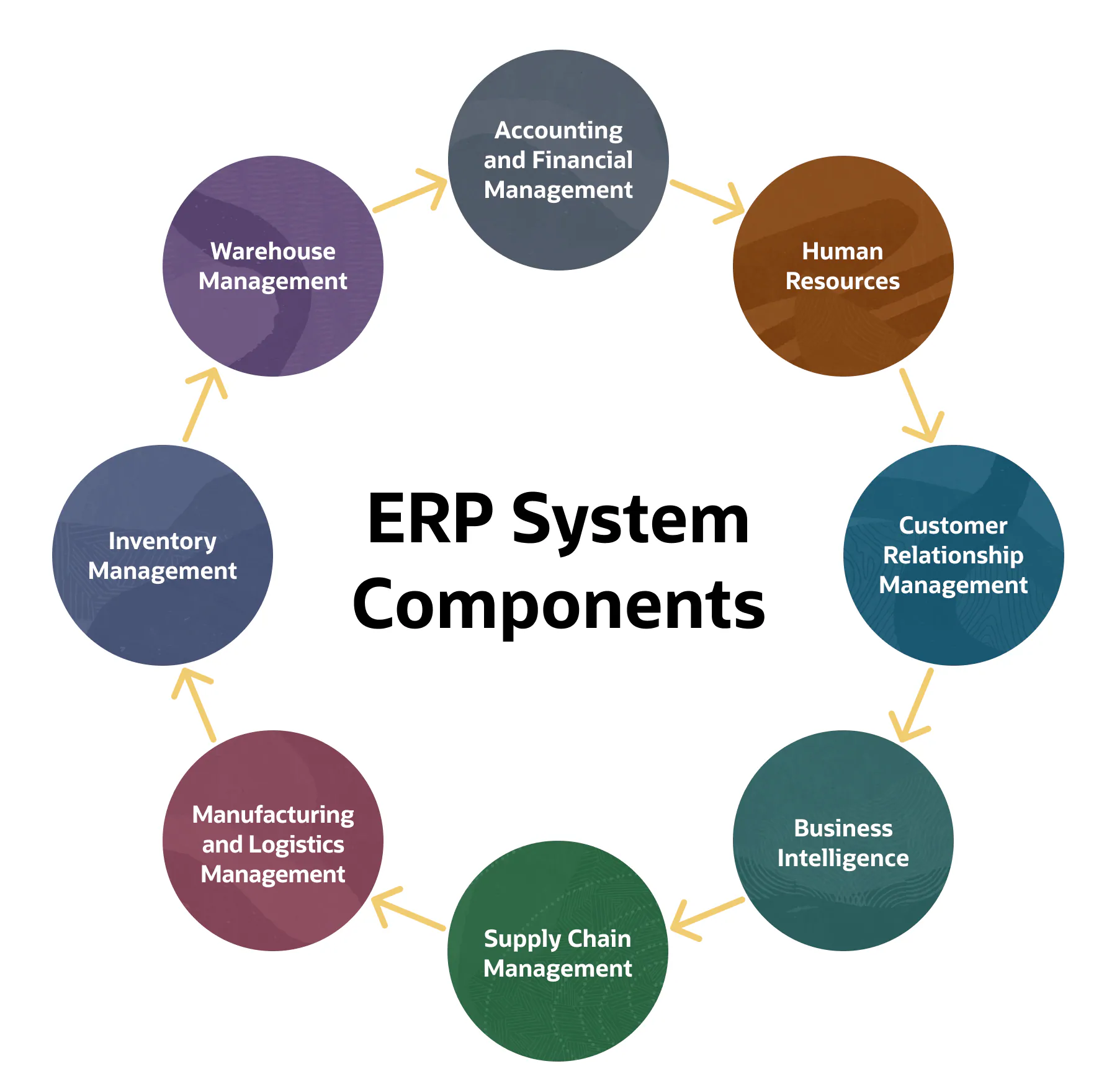
- Finance and Accounting: Managing financial transactions, reporting, budgeting and compliance.
- Human Resources (HR): Handling employee records, payroll, recruitment and performance management.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): Overseeing procurement, inventory management, production planning and logistics.
- Manufacturing: Managing production schedules, quality control and order fulfilment.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Tracking customer interactions, sales, support and marketing activities.
The primary goal of an ERP system is to provide a unified platform that integrates these diverse functions, there by improving coordination and providing a comprehensive view of business operations.
Core Features of ERP Systems
1. Integration
Integration is at the heart of ERP systems. By connecting various business functions, ERP systems eliminate the need for multiple, isolated software solutions. This integration ensures that data flows seamlessly between departments, reducing redundancy and enhancing accuracy. For example when a sales order is entered the system automatically updates inventory levels and financial records.
2. Real-Time Data
ERP systems provide real-time access to data across the organization. This feature is crucial for timely decision-making, allowing businesses to respond quickly to market changes, customer demands and operational issues. Real-time data ensures that stakeholders have the most current information, leading to more informed and effective decisions.
3. Automation
Automation is another significant feature of ERP systems. By automating routine tasks such as invoicing, payroll and order processing, ERP systems reduce the burden of manual work and minimize human error. This automation not only saves time but also ensures consistency and efficiency across various processes.
4. Scalability
Modern ERP systems are designed to scale with your business. Whether you’re expanding your workforce, entering new markets or adding new functionalities, an ERP system can adapt to your changing needs. This scalability ensures that the system remains relevant and effective as your business grows.
5. Customization
ERP systems offer a high degree of customization to meet the specific needs of different industries and business models. From configuring workflows to adapting reporting tools, customization ensures that the ERP system aligns with your unique processes and requirements.
Benefits of Implementing an ERP System

1. Increased Efficiency
One of the most significant benefits of an ERP system is the improvement in efficiency. By integrating various business functions and automating routine tasks, ERP systems streamline operations and reduce redundancy. This leads to faster processes, fewer errors and more efficient resource utilization.
2. Improved Decision-Making
Access to real-time data and comprehensive analytics enhances decision-making. With an ERP system, businesses can analyze trends, forecast needs and make strategic choices based on accurate and up-to-date information. This capability is crucial for staying competitive and responding effectively to market dynamics.
3. Cost Savings
ERP systems can lead to substantial cost savings by reducing manual intervention, improving accuracy and optimizing resource allocation. Automated processes cut down on labor costs and operational inefficiencies, while integrated data helps identify areas for cost reduction and process improvement.
4. Enhanced Customer Service
An ERP system improves customer service by providing a unified view of customer interactions and order statuses. With better access to customer information and streamlined order processing, businesses can respond more quickly to inquiries, fulfil orders more accurately and provide a better overall customer experience.
5. Regulatory Compliance
ERP systems help businesses stay compliant with industry regulations by providing robust tracking and reporting tools. From financial reporting to data security. ERP systems ensure that businesses meet regulatory requirements and maintain accurate records.
Challenges and Considerations
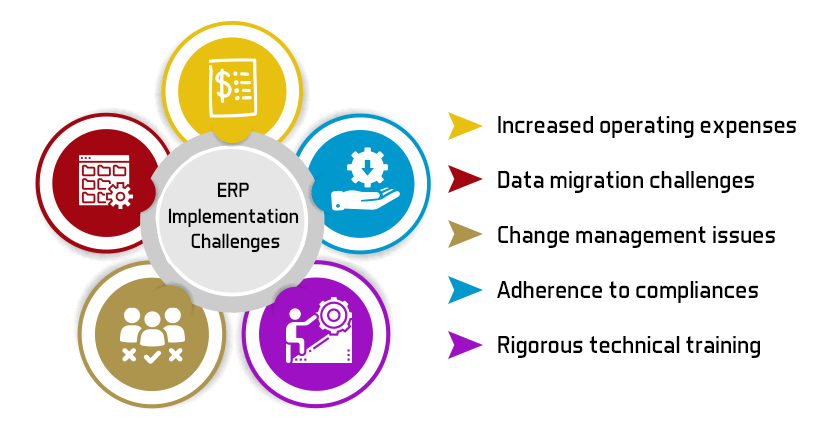
1. Cost of Implementation
The cost of implementing an ERP system can be substantial, including software licensing, hardware and consulting fees. Additionally, there may be costs associated with training employees and maintaining the system. Businesses need to carefully evaluate the return on investment and budget accordingly.
2. Complexity and Change Management
Implementing an ERP system is a complex process that involves significant changes to existing workflows and processes. Change management is crucial to ensure a smooth transition. This includes preparing employees for the new system, providing adequate training and managing any resistance to change.
3. Data Migration
Migrating data from legacy systems to a new ERP system can be challenging. Ensuring data accuracy and completeness is critical for the success of the implementation. Proper planning and execution are necessary to minimize disruptions and ensure a smooth data transition.
4. Customization and Integration
While ERP systems offer customization, extensive customization can increase complexity and cost. Additionally, integrating the ERP system with existing software and systems requires careful planning and technical expertise. Businesses should assess their customization needs and integration requirements before selecting an ERP solution.
5. Vendor Selection
Choosing the right ERP vendor is a critical decision. Factors to consider include the vendor’s reputation, customer support and track record. A reliable vendor can provide ongoing support, updates and assistance to ensure the success of the ERP implementation.
ERP Implementation Process
1. Planning and Analysis
The first step in the ERP implementation process is to plan and analyze your business needs. This involves defining the goals of the ERP system, assessing current processes and identifying any gaps or areas for improvement. Engaging stakeholders and creating a project plan are essential for a successful implementation.
2. System Selection
Based on your analysis, select an ERP system that aligns with your business needs. Evaluate different vendors, compare features and consider factors such as scalability, customization and cost. Involve key stakeholders in the selection process to ensure that the chosen system meets the requirements of various departments.
3. Data Migration and Integration
Prepare for data migration by cleansing and organizing data from legacy systems. Develop a strategy for transferring data to the new ERP system, ensuring accuracy and completeness. Additionally, plan for integrating the ERP system with other software and systems used by your organization.
4. Training and Change Management
Provide training for employees to ensure they understand how to use the new ERP system effectively. Implement change management strategies to address any resistance and facilitate a smooth transition. Clear communication and support are crucial for successful adoption.
5. Go-Live and Support
Once the system is configured and tested, go live with the ERP system. Monitor the system’s performance and provide ongoing support to address any issues that arise. Continuously evaluate the system’s effectiveness and make adjustments as needed to optimize performance.
Future Trends in ERP Systems
1. Cloud-Based ERP
Cloud-based ERP systems are becoming increasingly popular due to their flexibility, scalability and cost-effectiveness. Cloud ERP solutions offer the advantage of reduced IT infrastructure costs, automatic updates and accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are being integrated into ERP systems to enhance data analytics, automate decision-making and improve predictive capabilities. These technologies can provide valuable insights, optimize processes and support more informed decision-making.
3. Internet of Things (IoT)
The integration of IoT with ERP systems allows businesses to gather real-time data from connected devices and sensors. This data can be used to monitor equipment, track inventory and optimize operations. IoT-enabled ERP systems provide greater visibility and control over business processes.
4. Enhanced User Experience
User experience (UX) is a growing focus in ERP system development. Modern ERP systems are designed with intuitive interfaces, customizable dashboards and mobile access to improve usability and accessibility. A better user experience leads to higher adoption rates and more effective use of the system.
5. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is being explored for its potential to enhance data security, transparency and traceability in ERP systems. Blockchain can provide secure and immutable records of transactions, which is valuable for industries such as finance, supply chain and manufacturing.
Conclusion
ERP systems are powerful tools that integrate and automate core business processes, providing numerous benefits including increased efficiency, improved decision-making and cost savings. While implementing an ERP system involves challenges such as cost, complexity and data migration, careful planning and execution can lead to significant long-term advantages.
As technology continues to evolve, ERP systems are adapting to incorporate innovations such as cloud computing, AI, IoT, and blockchain. By staying informed about these trends and understanding the capabilities of ERP systems, businesses can leverage these tools to drive growth, optimize operations and stay competitive in a dynamic market.
In today’s fast-paced business environment the right ERP system can be a game-changer, helping organizations navigate complexity and achieve their strategic goals with greater agility and efficiency.





